The amount of data produced in a laboratory has been continuously increasing over the years.
Data are the documented evidence that pharmaceutical companies can use to demonstrate compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), but this is possible only if their integrity is ensured.
ALCOA+’s Data Integrity principles are met if the data are attributable, legible, contemporaneous, original, accurate, consistent and reliable throughout their entire life cycle, from generation to conservation and destruction, applicable to both paper and electronic data.
When we talk about Data Integrity today, the focus is no longer only on the data, awareness of which is the focal point, but also and especially on the computerized systems that generate electronic records.
However, there are still many laboratories that use paper data in spite of the risks involved: first, it is very easy to tamper with or falsify a paper data without a trace, and this aspect affects the reliability of the data; and secondly, it is very common to lose data, instrument output, logbooks, and worksheets both during the execution of the analyses and the retention of the records.
In addition, the time consumption for test preparation, execution, documentation and review before achieving batch release is considerable, and a large amount of paper is generated and must be stored for years, requiring sufficient space to ensure its retention.
What could you do to improve your laboratory data management?

Many companies are beginning to use a paperless approach to perform laboratory tests and record data, taking advantage of the benefits of using electronic records.
This is possible thanks to Electronic Laboratory Notebooks, which have been designed to enable a completely paperless environment for labs to record, execute and store test data. They provide a streamlined and human error-free environment for scientists, researchers, and Quality Control laboratories to record and archive their data, trace the executed operation and enforce the execution of activities with full 21 CFR Part 11 and regulations compliance.
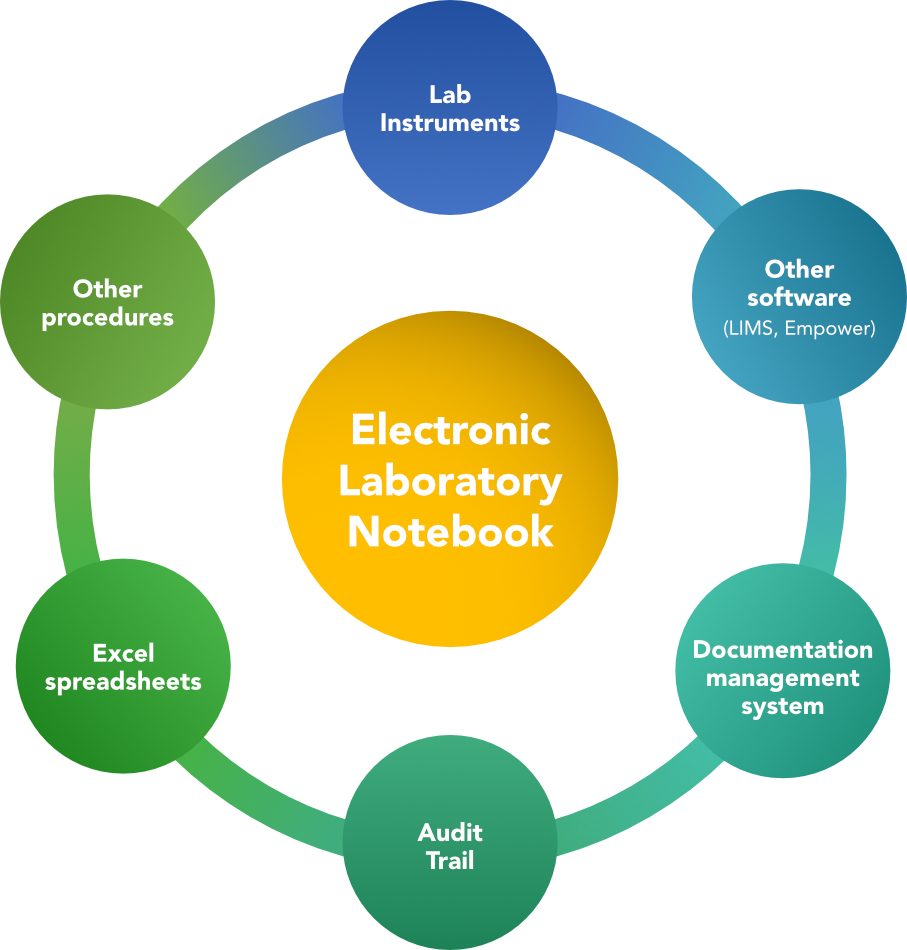
The use of an ELN allows organizations to reach the harmonization of processes within laboratories through:
- Method automation
This is achieved by translating the instructions of a method into an electronic format through the addition of specific commands, called scripts, that allow an analytical method to be executed by reading the instructions into the system and collecting the generated data necessary for reconstructing the tests, either by direct connection with instruments, other laboratory systems or by manual entry.
- Interface with lab instruments
Direct acquisition of raw data from the instruments, such as pH meter and balance, not only makes the test performance easier, but also allows for better data management and a reduced margin of error compared to paper recording, thanks in part to the presence of limit commands in accordance with the specifications of the method under analysis. This also avoids printing output receipts from the instruments that could easily get lost or altered.
- Interface with other software
Linking with chromatographic systems via Empower is particularly advantageous because the two systems communicate with each other, sending input and output information, thus facilitating the direct acquisition of analytical sequences and chromatographic results and also avoiding the printing of generated reports.
In parallel, the interface with the Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS) enables rapid and accurate documentation of the results obtained and keeps track of stability batches yet to be analyzed.
- Importation from other procedures
Information and data regarding calibration of instruments or preparation of solutions, mobile phases, and reagents can be imported from procedure to procedure.
- Excel spreadsheets
By interfacing with Excel, calculations to support analysis and generate results can be taken from spreadsheets.
- Audit trail applicability
The possibility to trace any changes, alteration or re-acquisition of data is always possible by reviewing the audit trail associated with each collected data.
The diagram below best summarizes these points and highlights the interconnections that can be made with an Electronic Laboratory Notebook:
What benefits do you get with ELN?
Electronic Laboratory Notebooks provide the best practices of data management to capture laboratory data consistently and share them efficiently.
ELNs simplify documentation and intellectual property protection, help operators collaborate in increasingly global and networked activities from production to analysis, and make scientific data and observations associated with analysis easier to acquire, search, find, and use.
Data to be provided during audits are easier and faster to find thanks to centralized archiving, and this helps with cooperating with inspectors as quickly as possible.
Each procedure created on the system is based on a standardized template, allowing raw data to be captured and processed in a step-by-step execution.
With a digital lab system, many of the lab's routine activities are simplified, from searching for previous work and planning tests to preparing and executing them and documenting and interpreting results.
They increase knowledge sharing and collaboration, eliminating the critical data management problem that afflicts paper-based labs, where up to 90 percent of data is used once and then lost or forgotten. Instead, with ENL up to 85 percent of data is reused. Unnecessary repetition of analysis is also reduced, making better use of limited resources.
In conclusion
Digitalization of laboratory data offers the best way forward and allows you to access data whenever you want, quickly and easily. It represents the right paper alternative solution that allows you to achieve simple workflows, time consumption savings, and a reduction in deviations!